-
1 circumlocution
a) using a roundabout form of expression instead of a simpler oneb) using a more or less complicated syntactical structure instead of a wordThey are classified into figurative periphrasis (metaphoric periphrasis or metonymic periphrasis) and logical periphrasis (euphemistic periphrasis)Source: V.A.K.••a device which, according to Webster's dictionary, denotes the use of a longer phrasing in place of a possible shorter and plainer form of expression- aims at pointing to one of the seemingly insignificant or barely noticeable features or properties of the given object, and intensifies this property by naming the object by the property;- makes the reader perceive the new appellation against the background of the one existing in the language code and the twofold simultaneous perception secures the stylistic effect;- like simile, has a certain cognitive function inasmuch as in deepens our knowledge of the phenomenon described;I understand you are poor, and wish to earn money by nursing the little boy, my son, who has so prematurely deprived of what can never be replaced. [= mother] (Ch.Dickens)
The lamp-lighter made his nightly failure in attempting to brighten up the street with gas. [= lit the street lamps] (Ch.Dickens)
If a periphrastic locution is understandable outside the context, it is not a stylistic device but merely a synonymous expression.the cap and gown (student body); a gentleman of the long robe (a lowyer); the fair sex (women); my better half (my wife)
Source: I.R.G.••троп, состоящий в замене названия предмета описательным оборотом с указанием его существенных, характерных признаков (I.V.A.)The beast that bears me. (horse) (W.Shakespeare - L)
English-Russian dictionary of stylistics (terminology and examples) > circumlocution
-
2 periphrasis
a) using a roundabout form of expression instead of a simpler oneb) using a more or less complicated syntactical structure instead of a wordThey are classified into figurative periphrasis (metaphoric periphrasis or metonymic periphrasis) and logical periphrasis (euphemistic periphrasis)Source: V.A.K.••a device which, according to Webster's dictionary, denotes the use of a longer phrasing in place of a possible shorter and plainer form of expression- aims at pointing to one of the seemingly insignificant or barely noticeable features or properties of the given object, and intensifies this property by naming the object by the property;- makes the reader perceive the new appellation against the background of the one existing in the language code and the twofold simultaneous perception secures the stylistic effect;- like simile, has a certain cognitive function inasmuch as in deepens our knowledge of the phenomenon described;I understand you are poor, and wish to earn money by nursing the little boy, my son, who has so prematurely deprived of what can never be replaced. [= mother] (Ch.Dickens)
The lamp-lighter made his nightly failure in attempting to brighten up the street with gas. [= lit the street lamps] (Ch.Dickens)
If a periphrastic locution is understandable outside the context, it is not a stylistic device but merely a synonymous expression.the cap and gown (student body); a gentleman of the long robe (a lowyer); the fair sex (women); my better half (my wife)
Source: I.R.G.••троп, состоящий в замене названия предмета описательным оборотом с указанием его существенных, характерных признаков (I.V.A.)The beast that bears me. (horse) (W.Shakespeare - L)
English-Russian dictionary of stylistics (terminology and examples) > periphrasis
-
3 classify
1. III1) classify smth., smb. classify books (units of any kind, plants, animals, people, etc.) классифицировать книги и т. д.2) classify smth. classify information (data, tools, etc.) засекретить информацию и т. д., объявить информацию и т. д. секретной2. IVclassify smb., smth. in some manner classify plants (animals, articles, subjects, etc.) carefully (exactly, broadly, conveniently, etc.) тщательно и т. д. классифицировать растения и т. д.3. XIbe classified in some manner this material (the data, words, etc.) must be carefully (exactly, etc.) classified этот материал и т. д. нужно тщательно и т. д. расклассифицировать; words can be classified in different ways (according to their meaning, into parts of speech, etc.) слова можно группировать /классифицировать/ по-разному и т. д;; in a library books are classified by subjects в библиотеках книги классифицируются по темам /систематизируются по тематическому принципу/4. XXI1classify smth., smb. into smth. classify words into groups (qualities into categories, plants into types, people into racial groups and subgroups, etc.) классифицировать /распределять/ слова по группам /разрядам/ и т. д.; one can broadly classify animals into wild and domestic всех животных можно грубо разделить на диких и домашних; classify smb, smth. by smth. classify people (children, soldiers, etc.) by age (by sex, by nationality, etc.) классифицировать /группировать/ людей и т. д. по возрасту и т. д.', classify books (articles, etc.) by languages (by subjects, by authors, etc.) распределять книги и т. д. по языкам и т. д. -
4 non-respondent
сущ.тж. nonrespondent соц. нереспондент (лицо, не участвовавшее в исследовании по каким-л. причинам)In practice, missing values are commonly encountered, which can be classified into two categories, namely, unit non-respondent and item non-respondent. — Как правило, на практике пропущенные данные встречаются. Они могут быть разделены на две категории: незаполненные анкеты и пропущенные вопросы.
See: -
5 approach and landing operations using instrument approach procedures
Instrument approach and landing operations are classified as follows:Non-precision approach and landing operations. An instrument approach and landing which utilizes lateral guidance but does not utilize vertical guidance.Approach and landing operations with vertical guidance. An instrument approach and landing which utilizes lateral and vertical guidance but does not meet the requirements established for precision approach and landing operations.Precision approach and landing operations. An instrument approach and landing using precision lateral and vertical guidance with minima as determined by the category of operation.Note.— Lateral and vertical guidance refers to the guidance provided either by:a) a ground-based navigation aid; orb) computer generated navigation data.Categories of precision approach and landing operations:Category I (CAT I) operation. A precision instrument approach and landing with a decision height not lower than 60 m (200 ft) and with either a visibility not less than 800 m or a runway visual range not less than 550 m.Category II (CAT II) operation. A precision instrument approach and landing with a decision height lower than 60 m (200 ft), but not lower than 30 m (100 ft), and a runway visual range not less than 350 m.Category IIIA (CAT IIIA) operation. A precision instrument approach and landing with:a) a decision height lower than 30 m (100 ft) or no decision height; andb) a runway visual range not less than 200 m.Category IIIB (CAT IIIB) operation. A precision instrument approach and landing with:a) a decision height lower than 15 m (50 ft) or no decision height; andb) a runway visual range less than 200 m but not less than 50 m.Category IIIC (CAT IIIC) operation. A precision instrument approach and landing with no decision height and no runway visual range limitations.Note.— Where decision height (DH) and runway visual range (RVR) fall into different categories of operation, the instrument approach and landing operation would be conducted in accordance with the requirements of the most demanding category (e.g. an operation with a DH in the range of CAT IIIA but with an RVR in the range of CAT IIIB would be considered a CAT IIIB operation or an operation with a DH in the range of CAT II but with an RVR in the range of CAT I would be considered a CAT II operation).(AN 6/I; AN 6/II; AN 6/III)заходы на посадку и посадки с использованием схем захода на посадку по приборамЗаходы на посадку и посадки по приборам классифицируются следующим образом:Неточные заходы на посадку и посадки. Заход на посадку и посадка по приборам с использованием бокового наведения, но без использования вертикального наведения.Заходы на посадку и посадки с вертикальным наведением. Заход на посадку и посадка по приборам с использованием бокового и вертикального наведения, но не отвечающие требованиям, установленным для точных заходов на посадку и посадок.Точные заходы на посадку и посадки. Заход на посадку и посадка по приборам с использованием точного бокового и вертикального наведения при минимумах, определяемых категорией захода на посадку и посадки.Примечание. Боковое и вертикальное наведение представляет собой наведение, обеспечиваемое с помощью либо:a) наземного навигационного средства, либоb) формируемых компьютером навигационных данных.Категории точных заходов на посадку и посадок:Категория I (кат. I). Точный заход на посадку и посадка по приборам с относительной высотой принятия решения не менее 60 м (200 фут) и либо при видимости не менее 800 м, либо при дальности видимости на ВПП не менее 550 м.Категория II (кат. II). Точый заход на посадку и посадка по приборам с относительной высотой принятия решения менее 60 м (200 фут), но не менее 30 м (100 фут) и при дальности видимости на ВПП не менее 350 м.Категория IIIA (кат. IIIA). Точный заход на посадку и посадка по приборам:a) с относительной высотой принятия решения менее 30 м (100 фут) или без ограничения по относительной высоте принятия решения иb) при дальности видимости на ВПП не менее 200 м.Категория IIIB (кат. IIIB). Точный заход на посадку и посадка по приборам:a) с относительной высотой принятия решения менее 15 м (50 фут) или без ограничения по относительной высоте принятия решения иb) при дальности видимости на ВПП менее 200 м, но не менее 50 м.Категория IIIC (кат. IIIC). Точный заход на посадку и посадка по приборам без ограничений по относительной высоте принятия решения и дальности видимости на ВПП.Примечание. Если относительная высота принятия решения (DH) и дальность видимости на ВПП (RVR) подпадают под разные категории, то заход на посадку и посадка по приборам будут выполняться в соответствии с требованияти самой жесткой категории (например, полёт с DH в диапазоне кат. IIIA, но при RVR в диапазоне кат. IIIB будет рассматриваться как полёт по кат. IIIB или полёт с DH в диапазоне кат. II, но при RVR в диапазоне кат. I будет рассматриваться как полёт по кат. II).International Civil Aviation Vocabulary (English-Russian) > approach and landing operations using instrument approach procedures
-
6 switchboard
- распределительный щит
- распределительное устройство
- НКУ распределения и управления
- коммутационный щит
- коммутаторная панель
- коммутатор
коммутатор
Устройство, обеспечивающее посредством включения, отключения и переключения электрических цепей выбор требуемой выходной цепи и соединение с ней входной цепи
[Терминологический словарь по строительству на 12 языках (ВНИИИС Госстроя СССР)]Тематики
- аппарат, изделие, устройство...
EN
DE
FR
коммутаторная панель
распределительный щит
Устройство, конструктивно объединяющее несколько коммутационных элементов, предназначенных для включения, отключения и переключения электрических цепей и каналов связи в ручном режиме.
[Л.М. Невдяев. Телекоммуникационные технологии. Англо-русский толковый словарь-справочник. Под редакцией Ю.М. Горностаева. Москва, 2002]Тематики
- электросвязь, основные понятия
Синонимы
EN
коммутационный щит
—
[Я.Н.Лугинский, М.С.Фези-Жилинская, Ю.С.Кабиров. Англо-русский словарь по электротехнике и электроэнергетике, Москва, 1999 г.]Тематики
- электротехника, основные понятия
EN
низковольтное устройство распределения и управления (НКУ)
Низковольтные коммутационные аппараты и устройства управления, измерения, сигнализации, защиты, регулирования, собранные совместно, со всеми внутренними электрическими и механическими соединениями и конструктивными элементами.
[ ГОСТ Р МЭК 61439-1-2012]
низковольтное устройство распределения и управления
Комбинация низковольтных коммутационных аппаратов с устройствами управления, измерения, сигнализации, защиты, регулирования и т. п., полностью смонтированных изготовителем НКУ (под его ответственность на единой конструктивной основе) со всеми внутренними электрическими и механическими соединениями с соответствующими конструктивными элементами
Примечания
1. В настоящем стандарте сокращение НКУ используют для обозначения низковольтных комплектных устройств распределения и управления.
2. Аппараты, входящие в состав НКУ, могут быть электромеханическими или электронными.
3. По различным причинам, например по условиям транспортирования или изготовления, некоторые операции сборки могут быть выполнены на месте установки, вне предприятия-изготовителя.
[ ГОСТ Р 51321. 1-2000 ( МЭК 60439-1-92)]EN
power switchgear and controlgear assembly (PSC-assembly)
low-voltage switchgear and controlgear assembly used to distribute and control energy for all types of loads, intended for industrial, commercial and similar applications where operation by ordinary persons is not intended
[IEC 61439-2, ed. 1.0 (2009-01)]
low-voltage switchgear and controlgear assembly
combination of one or more low-voltage switching devices together with associated control, measuring, signalling, protective, regulation equipment, etc., completely assembled under the responsibility of the manufacturer with all the internal electrical and mechanical interconnections and structural parts.
[IEC 61892-3, ed. 2.0 (2007-11)]
switchgear and controlgear
a general term covering switching devices and their combination with associated control, measuring, protective and regulating equipment, also assemblies of such devices and equipment with associated interconnections, accessories, enclosures and supporting structures
[IEV number 441-11-01]
switchgear and controlgear
electric equipment intended to be connected to an electric circuit for the purpose of carrying out one or more of the following functions: protection, control, isolation, switching
NOTE – The French and English terms can be considered as equivalent in most cases. However, the French term has a broader meaning than the English term and includes for example connecting devices, plugs and socket-outlets, etc. In English, these latter devices are known as accessories.
[IEV number 826-16-03 ]
switchboard
A large single electric control panel, frame, or assembly of panels on which are mounted (either on the back or on the face, or both) switches, overcurrent and other protective devices, buses, and usually instruments; not intended for installation in a cabinet but may be completely enclosed in metal; usually is accessible from both the front and rear.
[ McGraw-Hill Dictionary of Architecture & Construction]
switchboard
One or more panels accommodating control switches, indicators, and other apparatus for operating electric circuits
[ The American Heritage Dictionary of the English Language]FR
ensemble d'appareillage de puissance (ensemble PSC)
ensemble d'appareillage à basse tension utilisé pour répartir et commander l'énergie pour tous les types de charges et prévu pour des applications industrielles, commerciales et analogues dans lesquelles l'exploitation par des personnes ordinaires n'est pas prévue
[IEC 61439-2, ed. 1.0 (2009-01)]
appareillage, m
matériel électrique destiné à être relié à un circuit électrique en vue d'assurer une ou plusieurs des fonctions suivantes: protection, commande, sectionnement, connexion
NOTE – Les termes français et anglais peuvent être considérés comme équivalents dans la plupart des cas. Toutefois, le terme français couvre un domaine plus étendu que le terme anglais, et comprend notamment les dispositifs de connexion, les prises de courant, etc. En anglais, ces derniers sont dénommés "accessories".
[IEV number 826-16-03 ]
appareillage
terme général applicable aux appareils de connexion et à leur combinaison avec des appareils de commande, de mesure, de protection et de réglage qui leur sont associés, ainsi qu'aux ensembles de tels appareils avec les connexions, les accessoires, les enveloppes et les charpentes correspondantes
[IEV number 441-11-01]
A switchboard as defined in the National Electrical Code is a large single panel, frame, or assembly of panels on which are mounted, on the face or back or both switches, overcurrent and other protective devices, buses, and, usually, instruments.
Switchboards are generally accessible from the rear as well as from the front and are not intended to be installed in cabinets.
The types of switchboards, classified by basic features of construction, are as follows:
1. Live-front vertical panels
2. Dead-front boards
3. Safety enclosed boards( metal-clad)
[American electricians’ handbook]
The switchboard plays an essential role in the availability of electric power, while meeting the needs of personal and property safety.
Its definition, design and installation are based on precise rules; there is no place for improvisation.
The IEC 61439 standard aims to better define " low-voltage switchgear and controlgear assemblies", ensuring that the specified performances are reached.
It specifies in particular:
> the responsibilities of each player, distinguishing those of the original equipment manufacturer - the organization that performed the original design and associated verification of an assembly in accordance with the standard, and of the assembly manufacturer - the organization taking responsibility for the finished assembly;
> the design and verification rules, constituting a benchmark for product certification.
All the component parts of the electrical switchboard are concerned by the IEC 61439 standard.
Equipment produced in accordance with the requirements of this switchboard standard ensures the safety and reliability of the installation.
A switchboard must comply with the requirements of standard IEC 61439-1 and 2 to guarantee the safety and reliability of the installation.
Managers of installations, fully aware of the professional and legal liabilities weighing on their company and on themselves, demand a high level of safety for the electrical installation.
What is more, the serious economic consequences of prolonged halts in production mean that the electrical switchboard must provide excellent continuity of service, whatever the operating conditions.
[Schneider Electric]НКУ играет главную роль в обеспечении электроэнергией, удовлетворяя при этом всем требованиям по безопасности людей и сохранности имущества.
Выбор конструкции, проектирование и монтаж основаны на чётких правилах, не допускающих никакой импровизации.
Требования к низковольтным комплектным устройствам распределения и управления сформулированы в стандарте МЭК 61439 (ГОСТ Р 51321. 1-2000).
В частности, он определяет:
> распределение ответственности между изготовителем НКУ - организацией, разработавшей конструкцию НКУ и проверившей его на соответствие требованиям стандарта, и сборщиком – организацией, выполнившей сборку НКУ;
> конструкцию, технические характеристики, виды и методы испытаний НКУ.
В стандарте МЭК 61439 (ГОСТ Р 51321. 1-2000) описываются все компоненты НКУ.
Оборудование, изготовленное в соответствии с требованиями этого стандарта, обеспечивает безопасность и надежность электроустановки.
Для того чтобы гарантировать безопасность эксплуатации и надежность работы электроустановки, распределительный щит должен соответствовать требованиям стандарта МЭК 61439-1 и 2.
Лица, ответственные за электроустановки, должны быть полностью осведомлены о профессиональной и юридической ответственности, возложенной на их компанию и на них лично, за обеспечение высокого уровня безопасности эксплуатации этих электроустановок.
Кроме того, поскольку длительные перерывы производства приводят к серьезным экономическим последствиям, электрический распределительный щит должен обеспечивать надежную и бесперебойную работу независимо от условий эксплуатации.
[Перевод Интент]LV switchgear assemblies are undoubtedly the components of the electric installation more subject to the direct intervention of personnel (operations, maintenance, etc.) and for this reason users demand from them higher and higher safety requirements.
The compliance of an assembly with the state of the art and therefore, presumptively, with the relevant technical Standard, cannot be based only on the fact that the components which constitute it comply with the state of the art and therefore, at least presumptively, with the relevant technical standards.
In other words, the whole assembly must be designed, built and tested in compliance with the state of the art.
Since the assemblies under consideration are low voltage equipment, their rated voltage shall not exceed 1000 Va.c. or 1500 Vd.c. As regards currents, neither upper nor lower limits are provided in the application field of this Standard.
The Standard IEC 60439-1 states the construction, safety and maintenance requirements for low voltage switchgear and controlgear assemblies, without dealing with the functional aspects which remain a competence of the designer of the plant for which the assembly is intended.
[ABB]Низковольтные комплектные устройства (НКУ), вне всякого сомнения, являются частями электроустановок, которые наиболее подвержены непосредственному вмешательству оперативного, обслуживающего и т. п. персонала. Вот почему требования потребителей к безопасности НКУ становятся все выше и выше.
Соответствие НКУ современному положению дел и вследствие этого, гипотетически, соответствующим техническим стандартам, не может основываться только на том факте, что составляющие НКУ компоненты соответствуют современному состоянию дел и поэтому, по крайней мере, гипотетически, - соответствующим техническим стандартам
Другими словами, НКУ должно быть разработано, изготовлено и испытано в соответствии с современными требованиями.
Мы рассматриваем низковольтные комплектные устройства и это означает, что их номинальное напряжение не превышает 1000 В переменного тока или 1500 В постоянного тока. Что касается тока, то ни верхнее, ни нижнее значение стандартами, относящимися к данной области, не оговариваются
Стандарт МЭК 60439-1 устанавливает требования к конструкции, безопасности и техническому обслуживанию низковольтных комплектных устройств без учета их функций, полагая, что функции НКУ являются компетенцией проектировщиков электроустановки, частью которых эти НКУ являются.
[Перевод Интент]Тематики
- НКУ (шкафы, пульты,...)
Классификация
>>>Действия
Синонимы
Сопутствующие термины
EN
- assembly
- electrical switchboard
- low voltage controlgear and assembly
- low voltage switchboard
- low voltage switchgear and controlgear assembly
- low-voltage switchgear and controlgear assembly
- LV switchgear and controlgear assembly
- LV switchgear assembly
- panel
- power switchgear and controlgear assembly
- PSC-assembly
- switchboard
- switchgear and controlgear
- switchgear/controlgear
DE
- Schaltanlagen und/oder Schaltgeräte
FR
распределительное устройство
Распределительным устройством (РУ) называется электроустановка, служащая для приема и распределения электроэнергии и содержащая сборные и соединительные шины, коммутационные аппараты, вспомогательные устройства (компрессорные, аккумуляторные и др.), а также устройства защиты, автоматики и измерительные приборы.
[РД 34.20.185-94]
распределительное устройство
Электроустановка, предназначенная для приема и распределения электрической энергии на одном напряжении и содержащая коммутационные аппараты и соединяющие их сборные шины [секции шин], устройства управления и защиты.
Примечание. К устройствам управления относятся аппараты и связывающие их элементы обеспечивающие контроль, измерение, сигнализацию и выполнение команд.
[ ГОСТ 24291-90]
[ ГОСТ Р 53685-2009]
электрическое распределительное устройство
распределительное устройство
Устройство, предназначенное для приема и распределения электроэнергии на одном напряжении и содержащее коммутационные аппараты и соединяющие их сборные соединительные устройства.
Примечание. В состав распределительного устройства дополнительно могут входить устройства защиты и управления
[ОСТ 45.55-99]
распределительное устройство
Электроустановка, служащая для приема и распределения электроэнергии и содержащая коммутационные аппараты, сборные и соединительные шины, вспомогательные устройства (компрессорные, аккумуляторные и др.), а также устройства защиты, автоматики и измерительные приборы.
[ПОТ Р М-016-2001]
[РД 153-34.0-03.150-00]
устройство распределительное
Совокупность аппаратов и приборов для приёма и распределения электроэнергии одного напряжения, вырабатываемой электростанцией или преобразуемой подстанцией
[Терминологический словарь по строительству на 12 языках (ВНИИИС Госстроя СССР)]EN
switching substation
a substation which includes switchgear and usually busbars, but no power transformers
[IEV number 605-01-02]FR
poste de sectionnement
poste de coupure
poste comprenant des organes de manoeuvre et généralement des jeux de barres, à l'exclusion de transformateurs de puissance
[IEV number 605-01-02]В качестве РУ 6—10 кВ используется сборка высокого напряжения с однополюсными разъединителями и вертикальным расположением фаз одного присоединения и одна камера КСО с выключателем нагрузки и предохранителями для подключения трансформатора. Для РУ 0,4 кВ применяются сборки низкого напряжения с предохранителями и вертикальным расположением фаз одного присоединения.
На ПС применяются открытые (ОРУ), закрытые (ЗРУ) или комплектные (КРУ) распределительные устройства.
[ http://energy-ua.com/elektricheskie-p/klassifikatsiya.html]
В общем случае ПС и РУ являются составной частью электроустановок, которые различаются:
-
по назначению:
- генерирующие,
- преобразовательно-распределительные,
-
потребительские.
Генерирующие электроустановки служат для выработки электроэнергии, преобразовательно-распределительные электроустановки преобразуют электроэнергию в удобный для передачи и потребления вид, передают ее и распределяют между потребителями;
-
по роду тока:
- постоянного тока,
- переменного тока.
-
по напряжению:
- до 1000 В,
- выше 1000 В.
Шкала номинальных напряжений ограничена сравнительно небольшим числом стандартных значений, благодаря чему изготавливается небольшое число типоразмеров машин и оборудования, а электросети выполняются более экономичными. В установках трехфазного тока номинальным напряжением принято считать напряжение между фазами (междуфазовое напряжение). Согласно ГОСТ 29322—92 установлена следующая шкала номинальных напряжений:
для электросетей переменного тока частотой 50 Гц междуфазовое напряжение должно быть: 12, 24, 36, 42, 127, 220, 380 В; 3, 6, 10, 20, 35, 110, 150, 220, 330, 500, 750 и 1150 кВ;
для электросетей постоянного тока: 12, 24, 36, 48, 60, 110, 220, 440, 660, 825, 3000 В и выше.-
по способу присоединения к электросети ПС разделяются на:
- тупиковые (блочные),
- ответвительные (блочные),
- проходные (транзитные)
- узловые.
Тупиковые ПС получают питание по одной или двум тупиковым ВЛ.
Ответвительные ПС присоединяются ответвлением к одной или двум проходящим ВЛ с односторонним или двухсторонним питанием.
Проходные ПС включаются в рассечку одной или двух проходящих ВЛ с односторонним или двухсторонним питанием.
Узловые ПС кроме питающих имеют отходящие радиальные или транзитные ВЛ.-
по способу управления ПС могут быть:
- только с телесигнализацией,
- телеуправляемыми с телесигнализацией,
- с телесигнализацией и управлением с общеподстанционного пункта управления (ОПУ).
Подстанции оперативно обслуживаются постоянным дежурным персоналом на щите управления, дежурными на дому или оперативно-выездными бригадами (ОВБ). Ремонт ПС осуществляется специализированными выездными бригадами централизованного ремонта или местным персоналом подстанции.
В РУ напряжением до 1000 В провода, шины, аппараты, приборы и конструкции выбирают как по нормальным условиям работы (напряжению и току), так и по термическим и динамическим воздействиям токов коротких замыканий (КЗ) или предельно допустимой отключаемой мощности.
В РУ и ПС напряжением выше 1000 В расстояния между электрооборудованием, аппаратами, токоведущими частями, изоляторами, ограждениями и конструкциями устанавливаются так, чтобы при нормальном режиме работы электроустановки возникающие физические явления (температура нагрева, электрическая дуга, выброс газов, искрение и др.) не могли привести к повреждению оборудования и КЗ.[ http://energy-ua.com/elektricheskie-p/klassifikatsiya.html]
Several different classifications of switchgear can be made:- By the current rating.
-
By interrupting rating (maximum short circuit current that the device can safely interrupt)
- Circuit breakers can open and close on fault currents
- Load-break/Load-make switches can switch normal system load currents
- Isolators may only be operated while the circuit is dead, or the load current is very small.
-
By voltage class:
- Low voltage (less than 1,000 volts AC)
- Medium voltage (1,000–35,000 volts AC)
- High voltage (more than 35,000 volts AC)
-
By insulating medium:
-
By construction type:
- Indoor (further classified by IP (Ingress Protection) class or NEMA enclosure type)
- Outdoor
- Industrial
- Utility
- Marine
- Draw-out elements (removable without many tools)
- Fixed elements (bolted fasteners)
- Live-front
- Dead-front
- Open
- Metal-enclosed
- Metal-clad
- Metal enclosed & Metal clad
- Arc-resistant
-
By IEC degree of internal separation
- No Separation (Form 1)
- Busbars separated from functional units (Form 2a, 2b, 3a, 3b, 4a, 4b)
- Terminals for external conductors separated from busbars (Form 2b, 3b, 4a, 4b)
- Terminals for external conductors separated from functional units but not from each other (Form 3a, 3b)
- Functional units separated from each other (Form 3a, 3b, 4a, 4b)
- Terminals for external conductors separated from each other (Form 4a, 4b)
- Terminals for external conductors separate from their associated functional unit (Form 4b)
-
By interrupting device:
-
By operating method:
- Manually operated
- Motor/stored energy operated
- Solenoid operated
-
By type of current:
-
By application:
-
By purpose
- Isolating switches (disconnectors)
- Load-break switches.
- Grounding (earthing) switches
A single line-up may incorporate several different types of devices, for example, air-insulated bus, vacuum circuit breakers, and manually operated switches may all exist in the same row of cubicles.
Ratings, design, specifications and details of switchgear are set by a multitude of standards. In North America mostly IEEE and ANSI standards are used, much of the rest of the world uses IEC standards, sometimes with local national derivatives or variations.
[Robert W. Smeaton (ed) Switchgear and Control Handbook 3rd Ed., Mc Graw Hill, new York 1997]
[ http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/High_voltage_switchgear]Тематики
- электрификация, электроснабж. железных дорог
- электроагрегаты генераторные
- электробезопасность
- электроснабжение в целом
Синонимы
EN
- distribution
- energy distribution board
- gear
- switch-gear
- switchboard
- switchgear
- switching substation
- switchyard
DE
FR
распределительный щит
Комплектное устройство, содержащее различную коммутационную аппаратуру, соединенное с одной или более отходящими электрическими цепями, питающееся от одной или более входящих цепей, вместе с зажимами для присоединения нейтральных и защитных проводников.
[ ГОСТ Р МЭК 60050-826-2009]
щит распределительный
Электротехническое устройство, объединяющее коммутационную, регулирующую и защитную аппаратуру, а также контрольно-измерительные и сигнальные приборы
[Терминологический словарь по строительству на 12 языках (ВНИИИС Госстроя СССР)]
распределительный щит
—
[А.С.Гольдберг. Англо-русский энергетический словарь. 2006 г.]EN
distribution board
assembly containing different types of switchgear and controlgear associated with one or more outgoing electric circuits fed from one or more incoming electric circuits, together with terminals for the neutral and protective conductors.
[IEV number 826-16-08]FR
tableau de répartition, m
ensemble comportant différents types d'appareillage associés à un ou plusieurs circuits électriques de départ alimentés par un ou plusieurs circuits électriques d'arrivée, ainsi que des bornes pour les conducteurs neutre et de protection.
[IEV number 826-16-08]Distribution switchboards, including the Main LV Switchboard (MLVS), are critical to the dependability of an electrical installation. They must comply with well-defined standards governing the design and construction of LV switchgear assemblies
A distribution switchboard is the point at which an incoming-power supply divides into separate circuits, each of which is controlled and protected by the fuses or switchgear of the switchboard. A distribution switchboard is divided into a number of functional units, each comprising all the electrical and mechanical elements that contribute to the fulfilment of a given function. It represents a key link in the dependability chain.
Consequently, the type of distribution switchboard must be perfectly adapted to its application. Its design and construction must comply with applicable standards and working practises.
[Schneider Electric]Распределительные щиты, включая главный распределительный щит низкого напряжения (ГРЩ), играют решающую роль в обеспечении надежности электроустановки. Они должны отвечать требованиям соответствующих стандартов, определяющих конструкцию и порядок изготовления НКУ распределения электроэнергии.
В распределительном щите выполняется прием электроэнергии и ее распределение по отдельным цепям, каждая из которых контролируется и защищается плавкими предохранителями или автоматическими выключателями.
Распределительный щит состоит из функциональных блоков, включающих в себя все электрические и механические элементы, необходимые для выполнения требуемой функции. Распределительный щит представляет собой ключевое звено в цепи обеспечения надежности.
Тип распределительного щита должен соответствовать области применения. Конструкция и изготовление распределительного щита должны удовлетворять требованиям применимых стандартов и учитывать накопленную практику применения.
[Перевод Интент]
Рис. Schneider Electric
With Prisma Plus G you can be sure to build 100% Schneider Electric switchboards that are safe, optimised:
> All components (switchgear, distribution blocks, prefabricated connections, etc.) are perfectly rated and coordinated to work together;
> All switchboard configurations, even the most demanding ones, have been tested.
You can prove that your switchboard meets the current standards, at any time.
You can be sure to build a reliable electrical installation and give your customers full satisfaction in terms of dependability and safety for people and the installation.
Prisma Plus G with its discreet design, blends harmoniously into all tertiary and industrial buildings, including in entrance halls and passageways.
With Prisma Plus G you can build just the right switchboard for your customer, sized precisely to fit costs and needs.
With this complete, prefabricated and tested system, it's easy to upgrade your installation and still maintain the performance levels.
> The wall-mounted and floor-standing enclosures combine easily with switchboards already in service.
> Devices can be replaced or added at any time.
[Schneider Electric]С помощью оболочек Prisma Plus G можно создавать безопасные распределительные щиты, на 100 % состоящие из изделий Schneider Electric:
> все изделия (коммутационная аппаратура, распределительные блоки, готовые заводские соединения и т. д.) полностью совместимы механически и электрически;
> все варианты компоновки распределительных щитов, в том числе для наиболее ответственных применений, прошли испытания.В любое время вы можете доказать, что ваши распределительные щиты полностью соответствуют требованиям действующих стандартов.
Вы можете быть полностью уверены в том, что создаете надежные электроустановки, удовлетворяющие всем требованиям безопасности для людей и оборудования
Благодаря строгому дизайну, распределительные щиты Prisma Plus G гармонично сочетаются с интерьером любого общественного или промышленного здания. Они хорошо смотрятся и в вестибюле, и в коридоре.
Применяя оболочки Prisma Plus G можно создавать распределительные щиты, точно соответствующие требованиям заказчика как с точки зрения технических характеристик, так и стоимости.
С помощью данной испытанной системы, содержащей все необходимые компоненты заводского изготовления можно легко модернизировать существующую электроустановку и поддерживать её уровни производительности.> Навесные и напольные оболочки можно легко присоединить к уже эксплуатируемым распределительным щитам.
> Аппаратуру можно заменять или добавлять в любое время.
[Перевод Интент]The switchboard, central to the electrical installation.
Both the point of arrival of energy and a device for distribution to the site applications, the LV switchboard is the intelligence of the system, central to the electrical installation.
[Schneider Electric]Распределительный щит – «сердце» электроустановки.
Низковольтное комплектное устройство распределения является «сердцем» электроустановки, поскольку именно оно принимает электроэнергию из сети и распределяет её по территориально распределенным нагрузкам.
[Перевод Интент]Тематики
- НКУ (шкафы, пульты,...)
- электроснабжение в целом
EN
- branch distribution panel
- distributing board
- distributing panel
- distributing switchboard
- distribution bench
- distribution board
- distribution panel
- distribution switchboard
- gear
- keyboard
- PNL
- SB
- sw & d
- switchboard
- switchboard panel
DE
- elektrischer Verteiler, m
- Schalttafel
- Verteiler, m
FR
- tableau de distribution
- tableau de répartition, m
Англо-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > switchboard
-
7 near cash
!гос. фин. The resource budget contains a separate control total for “near cash” expenditure, that is expenditure such as pay and current grants which impacts directly on the measure of the golden rule.This paper provides background information on the framework for the planning and control of public expenditure in the UK which has been operated since the 1998 Comprehensive Spending Review (CSR). It sets out the different classifications of spending for budgeting purposes and why these distinctions have been adopted. It discusses how the public expenditure framework is designed to ensure both sound public finances and an outcome-focused approach to public expenditure.The UK's public spending framework is based on several key principles:"consistency with a long-term, prudent and transparent regime for managing the public finances as a whole;" "the judgement of success by policy outcomes rather than resource inputs;" "strong incentives for departments and their partners in service delivery to plan over several years and plan together where appropriate so as to deliver better public services with greater cost effectiveness; and"the proper costing and management of capital assets to provide the right incentives for public investment.The Government sets policy to meet two firm fiscal rules:"the Golden Rule states that over the economic cycle, the Government will borrow only to invest and not to fund current spending; and"the Sustainable Investment Rule states that net public debt as a proportion of GDP will be held over the economic cycle at a stable and prudent level. Other things being equal, net debt will be maintained below 40 per cent of GDP over the economic cycle.Achievement of the fiscal rules is assessed by reference to the national accounts, which are produced by the Office for National Statistics, acting as an independent agency. The Government sets its spending envelope to comply with these fiscal rules.Departmental Expenditure Limits ( DEL) and Annually Managed Expenditure (AME)"Departmental Expenditure Limit ( DEL) spending, which is planned and controlled on a three year basis in Spending Reviews; and"Annually Managed Expenditure ( AME), which is expenditure which cannot reasonably be subject to firm, multi-year limits in the same way as DEL. AME includes social security benefits, local authority self-financed expenditure, debt interest, and payments to EU institutions.More information about DEL and AME is set out below.In Spending Reviews, firm DEL plans are set for departments for three years. To ensure consistency with the Government's fiscal rules departments are set separate resource (current) and capital budgets. The resource budget contains a separate control total for “near cash” expenditure, that is expenditure such as pay and current grants which impacts directly on the measure of the golden rule.To encourage departments to plan over the medium term departments may carry forward unspent DEL provision from one year into the next and, subject to the normal tests for tautness and realism of plans, may be drawn down in future years. This end-year flexibility also removes any incentive for departments to use up their provision as the year end approaches with less regard to value for money. For the full benefits of this flexibility and of three year plans to feed through into improved public service delivery, end-year flexibility and three year budgets should be cascaded from departments to executive agencies and other budget holders.Three year budgets and end-year flexibility give those managing public services the stability to plan their operations on a sensible time scale. Further, the system means that departments cannot seek to bid up funds each year (before 1997, three year plans were set and reviewed in annual Public Expenditure Surveys). So the credibility of medium-term plans has been enhanced at both central and departmental level.Departments have certainty over the budgetary allocation over the medium term and these multi-year DEL plans are strictly enforced. Departments are expected to prioritise competing pressures and fund these within their overall annual limits, as set in Spending Reviews. So the DEL system provides a strong incentive to control costs and maximise value for money.There is a small centrally held DEL Reserve. Support from the Reserve is available only for genuinely unforeseeable contingencies which departments cannot be expected to manage within their DEL.AME typically consists of programmes which are large, volatile and demand-led, and which therefore cannot reasonably be subject to firm multi-year limits. The biggest single element is social security spending. Other items include tax credits, Local Authority Self Financed Expenditure, Scottish Executive spending financed by non-domestic rates, and spending financed from the proceeds of the National Lottery.AME is reviewed twice a year as part of the Budget and Pre-Budget Report process reflecting the close integration of the tax and benefit system, which was enhanced by the introduction of tax credits.AME is not subject to the same three year expenditure limits as DEL, but is still part of the overall envelope for public expenditure. Affordability is taken into account when policy decisions affecting AME are made. The Government has committed itself not to take policy measures which are likely to have the effect of increasing social security or other elements of AME without taking steps to ensure that the effects of those decisions can be accommodated prudently within the Government's fiscal rules.Given an overall envelope for public spending, forecasts of AME affect the level of resources available for DEL spending. Cautious estimates and the AME margin are built in to these AME forecasts and reduce the risk of overspending on AME.Together, DEL plus AME sum to Total Managed Expenditure (TME). TME is a measure drawn from national accounts. It represents the current and capital spending of the public sector. The public sector is made up of central government, local government and public corporations.Resource and Capital Budgets are set in terms of accruals information. Accruals information measures resources as they are consumed rather than when the cash is paid. So for example the Resource Budget includes a charge for depreciation, a measure of the consumption or wearing out of capital assets."Non cash charges in budgets do not impact directly on the fiscal framework. That may be because the national accounts use a different way of measuring the same thing, for example in the case of the depreciation of departmental assets. Or it may be that the national accounts measure something different: for example, resource budgets include a cost of capital charge reflecting the opportunity cost of holding capital; the national accounts include debt interest."Within the Resource Budget DEL, departments have separate controls on:"Near cash spending, the sub set of Resource Budgets which impacts directly on the Golden Rule; and"The amount of their Resource Budget DEL that departments may spend on running themselves (e.g. paying most civil servants’ salaries) is limited by Administration Budgets, which are set in Spending Reviews. Administration Budgets are used to ensure that as much money as practicable is available for front line services and programmes. These budgets also help to drive efficiency improvements in departments’ own activities. Administration Budgets exclude the costs of frontline services delivered directly by departments.The Budget preceding a Spending Review sets an overall envelope for public spending that is consistent with the fiscal rules for the period covered by the Spending Review. In the Spending Review, the Budget AME forecast for year one of the Spending Review period is updated, and AME forecasts are made for the later years of the Spending Review period.The 1998 Comprehensive Spending Review ( CSR), which was published in July 1998, was a comprehensive review of departmental aims and objectives alongside a zero-based analysis of each spending programme to determine the best way of delivering the Government's objectives. The 1998 CSR allocated substantial additional resources to the Government's key priorities, particularly education and health, for the three year period from 1999-2000 to 2001-02.Delivering better public services does not just depend on how much money the Government spends, but also on how well it spends it. Therefore the 1998 CSR introduced Public Service Agreements (PSAs). Each major government department was given its own PSA setting out clear targets for achievements in terms of public service improvements.The 1998 CSR also introduced the DEL/ AME framework for the control of public spending, and made other framework changes. Building on the investment and reforms delivered by the 1998 CSR, successive spending reviews in 2000, 2002 and 2004 have:"provided significant increase in resources for the Government’s priorities, in particular health and education, and cross-cutting themes such as raising productivity; extending opportunity; and building strong and secure communities;" "enabled the Government significantly to increase investment in public assets and address the legacy of under investment from past decades. Departmental Investment Strategies were introduced in SR2000. As a result there has been a steady increase in public sector net investment from less than ¾ of a per cent of GDP in 1997-98 to 2¼ per cent of GDP in 2005-06, providing better infrastructure across public services;" "introduced further refinements to the performance management framework. PSA targets have been reduced in number over successive spending reviews from around 300 to 110 to give greater focus to the Government’s highest priorities. The targets have become increasingly outcome-focused to deliver further improvements in key areas of public service delivery across Government. They have also been refined in line with the conclusions of the Devolving Decision Making Review to provide a framework which encourages greater devolution and local flexibility. Technical Notes were introduced in SR2000 explaining how performance against each PSA target will be measured; and"not only allocated near cash spending to departments, but also – since SR2002 - set Resource DEL plans for non cash spending.To identify what further investments and reforms are needed to equip the UK for the global challenges of the decade ahead, on 19 July 2005 the Chief Secretary to the Treasury announced that the Government intends to launch a second Comprehensive Spending Review (CSR) reporting in 2007.A decade on from the first CSR, the 2007 CSR will represent a long-term and fundamental review of government expenditure. It will cover departmental allocations for 2008-09, 2009-10 and 2010 11. Allocations for 2007-08 will be held to the agreed figures already announced by the 2004 Spending Review. To provide a rigorous analytical framework for these departmental allocations, the Government will be taking forward a programme of preparatory work over 2006 involving:"an assessment of what the sustained increases in spending and reforms to public service delivery have achieved since the first CSR. The assessment will inform the setting of new objectives for the decade ahead;" "an examination of the key long-term trends and challenges that will shape the next decade – including demographic and socio-economic change, globalisation, climate and environmental change, global insecurity and technological change – together with an assessment of how public services will need to respond;" "to release the resources needed to address these challenges, and to continue to secure maximum value for money from public spending over the CSR period, a set of zero-based reviews of departments’ baseline expenditure to assess its effectiveness in delivering the Government’s long-term objectives; together with"further development of the efficiency programme, building on the cross cutting areas identified in the Gershon Review, to embed and extend ongoing efficiency savings into departmental expenditure planning.The 2007 CSR also offers the opportunity to continue to refine the PSA framework so that it drives effective delivery and the attainment of ambitious national standards.Public Service Agreements (PSAs) were introduced in the 1998 CSR. They set out agreed targets detailing the outputs and outcomes departments are expected to deliver with the resources allocated to them. The new spending regime places a strong emphasis on outcome targets, for example in providing for better health and higher educational standards or service standards. The introduction in SR2004 of PSA ‘standards’ will ensure that high standards in priority areas are maintained.The Government monitors progress against PSA targets, and departments report in detail twice a year in their annual Departmental Reports (published in spring) and in their autumn performance reports. These reports provide Parliament and the public with regular updates on departments’ performance against their targets.Technical Notes explain how performance against each PSA target will be measured.To make the most of both new investment and existing assets, there needs to be a coherent long term strategy against which investment decisions are taken. Departmental Investment Strategies (DIS) set out each department's plans to deliver the scale and quality of capital stock needed to underpin its objectives. The DIS includes information about the department's existing capital stock and future plans for that stock, as well as plans for new investment. It also sets out the systems that the department has in place to ensure that it delivers its capital programmes effectively.This document was updated on 19 December 2005.Near-cash resource expenditure that has a related cash implication, even though the timing of the cash payment may be slightly different. For example, expenditure on gas or electricity supply is incurred as the fuel is used, though the cash payment might be made in arrears on aquarterly basis. Other examples of near-cash expenditure are: pay, rental.Net cash requirement the upper limit agreed by Parliament on the cash which a department may draw from theConsolidated Fund to finance the expenditure within the ambit of its Request forResources. It is equal to the agreed amount of net resources and net capital less non-cashitems and working capital.Non-cash cost costs where there is no cash transaction but which are included in a body’s accounts (or taken into account in charging for a service) to establish the true cost of all the resourcesused.Non-departmental a body which has a role in the processes of government, but is not a government public body, NDPBdepartment or part of one. NDPBs accordingly operate at arm’s length from governmentMinisters.Notional cost of a cost which is taken into account in setting fees and charges to improve comparability with insuranceprivate sector service providers.The charge takes account of the fact that public bodies donot generally pay an insurance premium to a commercial insurer.the independent body responsible for collecting and publishing official statistics about theUK’s society and economy. (At the time of going to print legislation was progressing tochange this body to the Statistics Board).Office of Government an office of the Treasury, with a status similar to that of an agency, which aims to maximise Commerce, OGCthe government’s purchasing power for routine items and combine professional expertiseto bear on capital projects.Office of the the government department responsible for discharging the Paymaster General’s statutoryPaymaster General,responsibilities to hold accounts and make payments for government departments and OPGother public bodies.Orange bookthe informal title for Management of Risks: Principles and Concepts, which is published by theTreasury for the guidance of public sector bodies.Office for NationalStatistics, ONS60Managing Public Money————————————————————————————————————————"GLOSSARYOverdraftan account with a negative balance.Parliament’s formal agreement to authorise an activity or expenditure.Prerogative powerspowers exercisable under the Royal Prerogative, ie powers which are unique to the Crown,as contrasted with common-law powers which may be available to the Crown on the samebasis as to natural persons.Primary legislationActs which have been passed by the Westminster Parliament and, where they haveappropriate powers, the Scottish Parliament and the Northern Ireland Assembly. Begin asBills until they have received Royal Assent.arrangements under which a public sector organisation contracts with a private sectorentity to construct a facility and provide associated services of a specified quality over asustained period. See annex 7.5.Proprietythe principle that patterns of resource consumption should respect Parliament’s intentions,conventions and control procedures, including any laid down by the PAC. See box 2.4.Public Accountssee Committee of Public Accounts.CommitteePublic corporationa trading body controlled by central government, local authority or other publiccorporation that has substantial day to day operating independence. See section 7.8.Public Dividend finance provided by government to public sector bodies as an equity stake; an alternative to Capital, PDCloan finance.Public Service sets out what the public can expect the government to deliver with its resources. EveryAgreement, PSAlarge government department has PSA(s) which specify deliverables as targets or aimsrelated to objectives.a structured arrangement between a public sector and a private sector organisation tosecure an outcome delivering good value for money for the public sector. It is classified tothe public or private sector according to which has more control.Rate of returnthe financial remuneration delivered by a particular project or enterprise, expressed as apercentage of the net assets employed.Regularitythe principle that resource consumption should accord with the relevant legislation, therelevant delegated authority and this document. See box 2.4.Request for the functional level into which departmental Estimates may be split. RfRs contain a number Resources, RfRof functions being carried out by the department in pursuit of one or more of thatdepartment’s objectives.Resource accountan accruals account produced in line with the Financial Reporting Manual (FReM).Resource accountingthe system under which budgets, Estimates and accounts are constructed in a similar wayto commercial audited accounts, so that both plans and records of expenditure allow in fullfor the goods and services which are to be, or have been, consumed – ie not just the cashexpended.Resource budgetthe means by which the government plans and controls the expenditure of resources tomeet its objectives.Restitutiona legal concept which allows money and property to be returned to its rightful owner. Ittypically operates where another person can be said to have been unjustly enriched byreceiving such monies.Return on capital the ratio of profit to capital employed of an accounting entity during an identified period.employed, ROCEVarious measures of profit and of capital employed may be used in calculating the ratio.Public Privatepartnership, PPPPrivate Finance Initiative, PFIParliamentaryauthority61Managing Public Money"————————————————————————————————————————GLOSSARYRoyal charterthe document setting out the powers and constitution of a corporation established underprerogative power of the monarch acting on Privy Council advice.Second readingthe second formal time that a House of Parliament may debate a bill, although in practicethe first substantive debate on its content. If successful, it is deemed to denoteParliamentary approval of the principle of the proposed legislation.Secondary legislationlaws, including orders and regulations, which are made using powers in primary legislation.Normally used to set out technical and administrative provision in greater detail thanprimary legislation, they are subject to a less intense level of scrutiny in Parliament.European legislation is,however,often implemented in secondary legislation using powers inthe European Communities Act 1972.Service-level agreement between parties, setting out in detail the level of service to be performed.agreementWhere agreements are between central government bodies, they are not legally a contractbut have a similar function.Shareholder Executive a body created to improve the government’s performance as a shareholder in businesses.Spending reviewsets out the key improvements in public services that the public can expect over a givenperiod. It includes a thorough review of departmental aims and objectives to find the bestway of delivering the government’s objectives, and sets out the spending plans for the givenperiod.State aidstate support for a domestic body or company which could distort EU competition and sois not usually allowed. See annex 4.9.Statement of Excessa formal statement detailing departments’ overspends prepared by the Comptroller andAuditor General as a result of undertaking annual audits.Statement on Internal an annual statement that Accounting Officers are required to make as part of the accounts Control, SICon a range of risk and control issues.Subheadindividual elements of departmental expenditure identifiable in Estimates as single cells, forexample cell A1 being administration costs within a particular line of departmental spending.Supplyresources voted by Parliament in response to Estimates, for expenditure by governmentdepartments.Supply Estimatesa statement of the resources the government needs in the coming financial year, and forwhat purpose(s), by which Parliamentary authority is sought for the planned level ofexpenditure and income.Target rate of returnthe rate of return required of a project or enterprise over a given period, usually at least a year.Third sectorprivate sector bodies which do not act commercially,including charities,social and voluntaryorganisations and other not-for-profit collectives. See annex 7.7.Total Managed a Treasury budgeting term which covers all current and capital spending carried out by the Expenditure,TMEpublic sector (ie not just by central departments).Trading fundan organisation (either within a government department or forming one) which is largely orwholly financed from commercial revenue generated by its activities. Its Estimate shows itsnet impact, allowing its income from receipts to be devoted entirely to its business.Treasury Minutea formal administrative document drawn up by the Treasury, which may serve a wide varietyof purposes including seeking Parliamentary approval for the use of receipts asappropriations in aid, a remission of some or all of the principal of voted loans, andresponding on behalf of the government to reports by the Public Accounts Committee(PAC).62Managing Public Money————————————————————————————————————————GLOSSARY63Managing Public MoneyValue for moneythe process under which organisation’s procurement, projects and processes aresystematically evaluated and assessed to provide confidence about suitability, effectiveness,prudence,quality,value and avoidance of error and other waste,judged for the public sectoras a whole.Virementthe process through which funds are moved between subheads such that additionalexpenditure on one is met by savings on one or more others.Votethe process by which Parliament approves funds in response to supply Estimates.Voted expenditureprovision for expenditure that has been authorised by Parliament. Parliament ‘votes’authority for public expenditure through the Supply Estimates process. Most expenditureby central government departments is authorised in this way.Wider market activity activities undertaken by central government organisations outside their statutory duties,using spare capacity and aimed at generating a commercial profit. See annex 7.6.Windfallmonies received by a department which were not anticipated in the spending review.———————————————————————————————————————— -
8 gear
- распределительный щит
- распределительное устройство
- оборудование
- инструменты
- входить в сцепление
- аппаратура
аппаратура
-
[Интент]FR
-
виды аппаратуры
- низковольтная аппаратура
- аппаратура распределения
- аппаратура управления
- аппаратура распределения и управления
- аппаратура для цепей управления
- коммутационная аппаратура
- контрльно-измерительная аппаратура (КИП)
- электронная аппаратура
- радиоэлектронная аппаратура
- закрытая аппаратура без вентиляции, охлаждаемая естественной конвекцией воздуха
- закрытая вентилируемая аппаратура
- открытая аппаратура
- периферийная аппаратура
- переносная аппаратура
- портативная аппаратура
Тематики
- аппарат, изделие, устройство...
EN
входить в сцепление
приводить в движение механизм
—
[ http://slovarionline.ru/anglo_russkiy_slovar_neftegazovoy_promyishlennosti/]Тематики
Синонимы
EN
инструменты
орудия
—
[ http://slovarionline.ru/anglo_russkiy_slovar_neftegazovoy_promyishlennosti/]Тематики
Синонимы
EN
оборудование
оборудование
Совокупность связанных между собой частей или устройств, из которых по крайней мере одно движется, а также элементы привода, управления и энергетические узлы, которые предназначены для определенного применения, в частности для обработки, производства, перемещения или упаковки материала. К термину «оборудование» относят также машину и совокупность машин, которые так устроены и управляемы, что они функционируют как единое целое для достижения одной и той же цели.
[ГОСТ ЕН 1070-2003]
-
[IEV number 151-11-25 ]
оборудование
Оснащение, материалы, приспособления, устройства, механизмы, приборы, инструменты и другие принадлежности, используемые в качестве частей электрической установки или в соединении с ней.
[ ГОСТ Р МЭК 60204-1-2007]EN
equipment
single apparatus or set of devices or apparatuses, or the set of main devices of an installation, or all devices necessary to perform a specific task
NOTE – Examples of equipment are a power transformer, the equipment of a substation, measuring equipment.
[IEV number 151-11-25 ]
equipment
material, fittings, devices, components, appliances, fixtures, apparatus, and the like used as part of, or in connection with, the electrical equipment of machines
[IEC 60204-1-2006]FR
équipement, m
matériel, m
appareil unique ou ensemble de dispositifs ou appareils, ou ensemble des dispositifs principaux d'une installation, ou ensemble des dispositifs nécessaires à l'accomplissement d'une tâche particulière
NOTE – Des exemples d’équipement ou de matériel sont un transformateur de puissance, l’équipement d’une sous-station, un équipement de mesure.
[IEV number 151-11-25]Тематики
EN
- accessories
- apparatus
- appliance
- assets
- environment
- equipment
- facility
- fitment
- fixing
- gear
- H/W
- hardware
- hardware environment
- HW
- installation
- instrument
- instrumentation
- layout
- machinery
- outfit
- paraphernalia
- plant
- plant stock
- product
- provisions
- rig
- rigging
- set-up
- stock-in-trade
- tackle
- technical equipment
- technique
DE
FR
- machine
- matériel, m
- équipement, m
распределительное устройство
Распределительным устройством (РУ) называется электроустановка, служащая для приема и распределения электроэнергии и содержащая сборные и соединительные шины, коммутационные аппараты, вспомогательные устройства (компрессорные, аккумуляторные и др.), а также устройства защиты, автоматики и измерительные приборы.
[РД 34.20.185-94]
распределительное устройство
Электроустановка, предназначенная для приема и распределения электрической энергии на одном напряжении и содержащая коммутационные аппараты и соединяющие их сборные шины [секции шин], устройства управления и защиты.
Примечание. К устройствам управления относятся аппараты и связывающие их элементы обеспечивающие контроль, измерение, сигнализацию и выполнение команд.
[ ГОСТ 24291-90]
[ ГОСТ Р 53685-2009]
электрическое распределительное устройство
распределительное устройство
Устройство, предназначенное для приема и распределения электроэнергии на одном напряжении и содержащее коммутационные аппараты и соединяющие их сборные соединительные устройства.
Примечание. В состав распределительного устройства дополнительно могут входить устройства защиты и управления
[ОСТ 45.55-99]
распределительное устройство
Электроустановка, служащая для приема и распределения электроэнергии и содержащая коммутационные аппараты, сборные и соединительные шины, вспомогательные устройства (компрессорные, аккумуляторные и др.), а также устройства защиты, автоматики и измерительные приборы.
[ПОТ Р М-016-2001]
[РД 153-34.0-03.150-00]
устройство распределительное
Совокупность аппаратов и приборов для приёма и распределения электроэнергии одного напряжения, вырабатываемой электростанцией или преобразуемой подстанцией
[Терминологический словарь по строительству на 12 языках (ВНИИИС Госстроя СССР)]EN
switching substation
a substation which includes switchgear and usually busbars, but no power transformers
[IEV number 605-01-02]FR
poste de sectionnement
poste de coupure
poste comprenant des organes de manoeuvre et généralement des jeux de barres, à l'exclusion de transformateurs de puissance
[IEV number 605-01-02]В качестве РУ 6—10 кВ используется сборка высокого напряжения с однополюсными разъединителями и вертикальным расположением фаз одного присоединения и одна камера КСО с выключателем нагрузки и предохранителями для подключения трансформатора. Для РУ 0,4 кВ применяются сборки низкого напряжения с предохранителями и вертикальным расположением фаз одного присоединения.
На ПС применяются открытые (ОРУ), закрытые (ЗРУ) или комплектные (КРУ) распределительные устройства.
[ http://energy-ua.com/elektricheskie-p/klassifikatsiya.html]
В общем случае ПС и РУ являются составной частью электроустановок, которые различаются:
-
по назначению:
- генерирующие,
- преобразовательно-распределительные,
-
потребительские.
Генерирующие электроустановки служат для выработки электроэнергии, преобразовательно-распределительные электроустановки преобразуют электроэнергию в удобный для передачи и потребления вид, передают ее и распределяют между потребителями;
-
по роду тока:
- постоянного тока,
- переменного тока.
-
по напряжению:
- до 1000 В,
- выше 1000 В.
Шкала номинальных напряжений ограничена сравнительно небольшим числом стандартных значений, благодаря чему изготавливается небольшое число типоразмеров машин и оборудования, а электросети выполняются более экономичными. В установках трехфазного тока номинальным напряжением принято считать напряжение между фазами (междуфазовое напряжение). Согласно ГОСТ 29322—92 установлена следующая шкала номинальных напряжений:
для электросетей переменного тока частотой 50 Гц междуфазовое напряжение должно быть: 12, 24, 36, 42, 127, 220, 380 В; 3, 6, 10, 20, 35, 110, 150, 220, 330, 500, 750 и 1150 кВ;
для электросетей постоянного тока: 12, 24, 36, 48, 60, 110, 220, 440, 660, 825, 3000 В и выше.-
по способу присоединения к электросети ПС разделяются на:
- тупиковые (блочные),
- ответвительные (блочные),
- проходные (транзитные)
- узловые.
Тупиковые ПС получают питание по одной или двум тупиковым ВЛ.
Ответвительные ПС присоединяются ответвлением к одной или двум проходящим ВЛ с односторонним или двухсторонним питанием.
Проходные ПС включаются в рассечку одной или двух проходящих ВЛ с односторонним или двухсторонним питанием.
Узловые ПС кроме питающих имеют отходящие радиальные или транзитные ВЛ.-
по способу управления ПС могут быть:
- только с телесигнализацией,
- телеуправляемыми с телесигнализацией,
- с телесигнализацией и управлением с общеподстанционного пункта управления (ОПУ).
Подстанции оперативно обслуживаются постоянным дежурным персоналом на щите управления, дежурными на дому или оперативно-выездными бригадами (ОВБ). Ремонт ПС осуществляется специализированными выездными бригадами централизованного ремонта или местным персоналом подстанции.
В РУ напряжением до 1000 В провода, шины, аппараты, приборы и конструкции выбирают как по нормальным условиям работы (напряжению и току), так и по термическим и динамическим воздействиям токов коротких замыканий (КЗ) или предельно допустимой отключаемой мощности.
В РУ и ПС напряжением выше 1000 В расстояния между электрооборудованием, аппаратами, токоведущими частями, изоляторами, ограждениями и конструкциями устанавливаются так, чтобы при нормальном режиме работы электроустановки возникающие физические явления (температура нагрева, электрическая дуга, выброс газов, искрение и др.) не могли привести к повреждению оборудования и КЗ.[ http://energy-ua.com/elektricheskie-p/klassifikatsiya.html]
Several different classifications of switchgear can be made:- By the current rating.
-
By interrupting rating (maximum short circuit current that the device can safely interrupt)
- Circuit breakers can open and close on fault currents
- Load-break/Load-make switches can switch normal system load currents
- Isolators may only be operated while the circuit is dead, or the load current is very small.
-
By voltage class:
- Low voltage (less than 1,000 volts AC)
- Medium voltage (1,000–35,000 volts AC)
- High voltage (more than 35,000 volts AC)
-
By insulating medium:
-
By construction type:
- Indoor (further classified by IP (Ingress Protection) class or NEMA enclosure type)
- Outdoor
- Industrial
- Utility
- Marine
- Draw-out elements (removable without many tools)
- Fixed elements (bolted fasteners)
- Live-front
- Dead-front
- Open
- Metal-enclosed
- Metal-clad
- Metal enclosed & Metal clad
- Arc-resistant
-
By IEC degree of internal separation
- No Separation (Form 1)
- Busbars separated from functional units (Form 2a, 2b, 3a, 3b, 4a, 4b)
- Terminals for external conductors separated from busbars (Form 2b, 3b, 4a, 4b)
- Terminals for external conductors separated from functional units but not from each other (Form 3a, 3b)
- Functional units separated from each other (Form 3a, 3b, 4a, 4b)
- Terminals for external conductors separated from each other (Form 4a, 4b)
- Terminals for external conductors separate from their associated functional unit (Form 4b)
-
By interrupting device:
-
By operating method:
- Manually operated
- Motor/stored energy operated
- Solenoid operated
-
By type of current:
-
By application:
-
By purpose
- Isolating switches (disconnectors)
- Load-break switches.
- Grounding (earthing) switches
A single line-up may incorporate several different types of devices, for example, air-insulated bus, vacuum circuit breakers, and manually operated switches may all exist in the same row of cubicles.
Ratings, design, specifications and details of switchgear are set by a multitude of standards. In North America mostly IEEE and ANSI standards are used, much of the rest of the world uses IEC standards, sometimes with local national derivatives or variations.
[Robert W. Smeaton (ed) Switchgear and Control Handbook 3rd Ed., Mc Graw Hill, new York 1997]
[ http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/High_voltage_switchgear]Тематики
- электрификация, электроснабж. железных дорог
- электроагрегаты генераторные
- электробезопасность
- электроснабжение в целом
Синонимы
EN
- distribution
- energy distribution board
- gear
- switch-gear
- switchboard
- switchgear
- switching substation
- switchyard
DE
FR
распределительный щит
Комплектное устройство, содержащее различную коммутационную аппаратуру, соединенное с одной или более отходящими электрическими цепями, питающееся от одной или более входящих цепей, вместе с зажимами для присоединения нейтральных и защитных проводников.
[ ГОСТ Р МЭК 60050-826-2009]
щит распределительный
Электротехническое устройство, объединяющее коммутационную, регулирующую и защитную аппаратуру, а также контрольно-измерительные и сигнальные приборы
[Терминологический словарь по строительству на 12 языках (ВНИИИС Госстроя СССР)]
распределительный щит
—
[А.С.Гольдберг. Англо-русский энергетический словарь. 2006 г.]EN
distribution board
assembly containing different types of switchgear and controlgear associated with one or more outgoing electric circuits fed from one or more incoming electric circuits, together with terminals for the neutral and protective conductors.
[IEV number 826-16-08]FR
tableau de répartition, m
ensemble comportant différents types d'appareillage associés à un ou plusieurs circuits électriques de départ alimentés par un ou plusieurs circuits électriques d'arrivée, ainsi que des bornes pour les conducteurs neutre et de protection.
[IEV number 826-16-08]Distribution switchboards, including the Main LV Switchboard (MLVS), are critical to the dependability of an electrical installation. They must comply with well-defined standards governing the design and construction of LV switchgear assemblies
A distribution switchboard is the point at which an incoming-power supply divides into separate circuits, each of which is controlled and protected by the fuses or switchgear of the switchboard. A distribution switchboard is divided into a number of functional units, each comprising all the electrical and mechanical elements that contribute to the fulfilment of a given function. It represents a key link in the dependability chain.
Consequently, the type of distribution switchboard must be perfectly adapted to its application. Its design and construction must comply with applicable standards and working practises.
[Schneider Electric]Распределительные щиты, включая главный распределительный щит низкого напряжения (ГРЩ), играют решающую роль в обеспечении надежности электроустановки. Они должны отвечать требованиям соответствующих стандартов, определяющих конструкцию и порядок изготовления НКУ распределения электроэнергии.
В распределительном щите выполняется прием электроэнергии и ее распределение по отдельным цепям, каждая из которых контролируется и защищается плавкими предохранителями или автоматическими выключателями.
Распределительный щит состоит из функциональных блоков, включающих в себя все электрические и механические элементы, необходимые для выполнения требуемой функции. Распределительный щит представляет собой ключевое звено в цепи обеспечения надежности.
Тип распределительного щита должен соответствовать области применения. Конструкция и изготовление распределительного щита должны удовлетворять требованиям применимых стандартов и учитывать накопленную практику применения.
[Перевод Интент]
Рис. Schneider Electric
With Prisma Plus G you can be sure to build 100% Schneider Electric switchboards that are safe, optimised:
> All components (switchgear, distribution blocks, prefabricated connections, etc.) are perfectly rated and coordinated to work together;
> All switchboard configurations, even the most demanding ones, have been tested.
You can prove that your switchboard meets the current standards, at any time.
You can be sure to build a reliable electrical installation and give your customers full satisfaction in terms of dependability and safety for people and the installation.
Prisma Plus G with its discreet design, blends harmoniously into all tertiary and industrial buildings, including in entrance halls and passageways.
With Prisma Plus G you can build just the right switchboard for your customer, sized precisely to fit costs and needs.
With this complete, prefabricated and tested system, it's easy to upgrade your installation and still maintain the performance levels.
> The wall-mounted and floor-standing enclosures combine easily with switchboards already in service.
> Devices can be replaced or added at any time.
[Schneider Electric]С помощью оболочек Prisma Plus G можно создавать безопасные распределительные щиты, на 100 % состоящие из изделий Schneider Electric:
> все изделия (коммутационная аппаратура, распределительные блоки, готовые заводские соединения и т. д.) полностью совместимы механически и электрически;
> все варианты компоновки распределительных щитов, в том числе для наиболее ответственных применений, прошли испытания.В любое время вы можете доказать, что ваши распределительные щиты полностью соответствуют требованиям действующих стандартов.
Вы можете быть полностью уверены в том, что создаете надежные электроустановки, удовлетворяющие всем требованиям безопасности для людей и оборудования
Благодаря строгому дизайну, распределительные щиты Prisma Plus G гармонично сочетаются с интерьером любого общественного или промышленного здания. Они хорошо смотрятся и в вестибюле, и в коридоре.
Применяя оболочки Prisma Plus G можно создавать распределительные щиты, точно соответствующие требованиям заказчика как с точки зрения технических характеристик, так и стоимости.
С помощью данной испытанной системы, содержащей все необходимые компоненты заводского изготовления можно легко модернизировать существующую электроустановку и поддерживать её уровни производительности.> Навесные и напольные оболочки можно легко присоединить к уже эксплуатируемым распределительным щитам.
> Аппаратуру можно заменять или добавлять в любое время.
[Перевод Интент]The switchboard, central to the electrical installation.
Both the point of arrival of energy and a device for distribution to the site applications, the LV switchboard is the intelligence of the system, central to the electrical installation.
[Schneider Electric]Распределительный щит – «сердце» электроустановки.
Низковольтное комплектное устройство распределения является «сердцем» электроустановки, поскольку именно оно принимает электроэнергию из сети и распределяет её по территориально распределенным нагрузкам.
[Перевод Интент]Тематики
- НКУ (шкафы, пульты,...)
- электроснабжение в целом
EN
- branch distribution panel
- distributing board
- distributing panel
- distributing switchboard
- distribution bench
- distribution board
- distribution panel
- distribution switchboard
- gear
- keyboard
- PNL
- SB
- sw & d
- switchboard
- switchboard panel
DE
- elektrischer Verteiler, m
- Schalttafel
- Verteiler, m
FR
- tableau de distribution
- tableau de répartition, m
Англо-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > gear
-
9 REACH (Registration, Evaluation and Authorisation of Chemicals) regulation EC/1907/2006
регламент ЕС № 1907/2006, касающийся правил регистрации, оценки, санкционирования и ограничения химических веществ (REACH)
-Параллельные тексты EN-RU REACH (Registration, Evaluation and Authorisation of Chemicals) regulation EC/1907/2006
In Europe, the purpose of the REACH regulation EC/1907/2006, which came into force on 1 June 2007, is to give the public better protection against chemicals that are available on the market and to make good the lack of knowledge about these chemicals.
Initially this regulation made manufacturers and importers of chemicals responsible for providing information on the safety of these substances for health and the environment and the uses made of them: this is the registration phase, which is the basis of the REACH system.
At the same time the function of the REACH regulation is to set up a framework for controlling the risks associated with the use of dangerous substances.
Certain substances may therefore be subject to usage restrictions or may even be prohibited.
Manufacturers and importers of chemicals must obtain authorisation to use substances classified in the “substance of very high concern” category.
A substance could be classified in this category if there is a risk for human health and/or the environment.
The aim of this Authorisation is to assure that the risks from substances of very high concern are properly controlled and that these substances are progressively replaced by suitable alternative substances.
[Legrand]Регламент ЕС № 1907/2006, касающийся правил регистрации, оценки, санкционирования и ограничения химических веществ (REACH)
Целью введения европейского регламента ЕС № 1907/2006 (REACH), вступившего в силу 1 июня 2007 года, является обеспечение более высокого уровня безопасности потребителей при использовании имеющихся на рынке химических веществ и предоставление отсутствовавшей ранее информации по этим химическим веществам.
В первую очередь данная норма обязала изготовителей и импортеров предоставлять информацию о безопасности химических веществ и их соединений, в отношении здоровья людей и окружающей среды. Информация предоставляется на этапе регистрации, которая лежит в основе системы REACH.
В то же время задача регламента REACH заключается в создании структуры для управления рисками, связанными с использованием опасных веществ.
В отношении некоторых веществ могут быть введены определенные ограничения использования. Какие-то вещества могут быть запрещены.
Изготовители и импортеры должны получать разрешение на использование веществ, отнесенных к категории «особо опасные вещества».
К данной категории относят вещества, представляющие опасность для здоровья человека и/или окружающей среды.
Целью такого санкционирования является обеспечение надлежащего контроля за веществами, относящихся к категории «особо опасные» и постепенная замена этих веществ альтернативными.
[Перевод Интент]Синонимы
- регламент ЕС № 1907/2006, касающийся правил регистрации, оценки, санкционирования и ограничения химических веществ (REACH)
EN
- REACH (Registration, Evaluation and Authorisation of Chemicals) regulation EC/1907/2006
- REACH regulation
Англо-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > REACH (Registration, Evaluation and Authorisation of Chemicals) regulation EC/1907/2006
-
10 REACH regulation
регламент ЕС № 1907/2006, касающийся правил регистрации, оценки, санкционирования и ограничения химических веществ (REACH)
-Параллельные тексты EN-RU REACH (Registration, Evaluation and Authorisation of Chemicals) regulation EC/1907/2006
In Europe, the purpose of the REACH regulation EC/1907/2006, which came into force on 1 June 2007, is to give the public better protection against chemicals that are available on the market and to make good the lack of knowledge about these chemicals.
Initially this regulation made manufacturers and importers of chemicals responsible for providing information on the safety of these substances for health and the environment and the uses made of them: this is the registration phase, which is the basis of the REACH system.
At the same time the function of the REACH regulation is to set up a framework for controlling the risks associated with the use of dangerous substances.
Certain substances may therefore be subject to usage restrictions or may even be prohibited.
Manufacturers and importers of chemicals must obtain authorisation to use substances classified in the “substance of very high concern” category.
A substance could be classified in this category if there is a risk for human health and/or the environment.
The aim of this Authorisation is to assure that the risks from substances of very high concern are properly controlled and that these substances are progressively replaced by suitable alternative substances.
[Legrand]Регламент ЕС № 1907/2006, касающийся правил регистрации, оценки, санкционирования и ограничения химических веществ (REACH)
Целью введения европейского регламента ЕС № 1907/2006 (REACH), вступившего в силу 1 июня 2007 года, является обеспечение более высокого уровня безопасности потребителей при использовании имеющихся на рынке химических веществ и предоставление отсутствовавшей ранее информации по этим химическим веществам.
В первую очередь данная норма обязала изготовителей и импортеров предоставлять информацию о безопасности химических веществ и их соединений, в отношении здоровья людей и окружающей среды. Информация предоставляется на этапе регистрации, которая лежит в основе системы REACH.
В то же время задача регламента REACH заключается в создании структуры для управления рисками, связанными с использованием опасных веществ.
В отношении некоторых веществ могут быть введены определенные ограничения использования. Какие-то вещества могут быть запрещены.
Изготовители и импортеры должны получать разрешение на использование веществ, отнесенных к категории «особо опасные вещества».
К данной категории относят вещества, представляющие опасность для здоровья человека и/или окружающей среды.
Целью такого санкционирования является обеспечение надлежащего контроля за веществами, относящихся к категории «особо опасные» и постепенная замена этих веществ альтернативными.
[Перевод Интент]Синонимы
- регламент ЕС № 1907/2006, касающийся правил регистрации, оценки, санкционирования и ограничения химических веществ (REACH)
EN
- REACH (Registration, Evaluation and Authorisation of Chemicals) regulation EC/1907/2006
- REACH regulation
Англо-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > REACH regulation
-
11 power center
главный распределительный щит (ГРЩ)
Распределительный щит, через который снабжается электроэнергией все здание или его обособленная часть. Роль ГРЩ может выполнять ВРУ или щит низкого напряжения подстанции.
[ПУЭ]
главный распределительный щит
Электрощит в здании, обеспечивающий распределение энергии между подключенными к нему нагрузками и включение аварийных систем при падении напряжения.
[ ГОСТ Р 51321. 3-99 ( МЭК 60439-3-90)]
[ ГОСТ Р 50571.28-2006]EN
main distribution board
board in the building which fulfils all the functions of a main electrical distribution for the supply building area assigned to it and where the voltage drop is measured for operating the safety services
[IEC 60364-7-710, ed. 1.0 (2002-11)]FR
tableau général de distribution
tableau de distribution dans le bâtiment remplissant toutes les fonctions d’un tableau général de distribution pour l’alimentation de la zone qui lui est dédiée et où la chute de tension est mesurée pour le fonctionnement des services de sécurité
[IEC 60364-7-710, ed. 1.0 (2002-11)]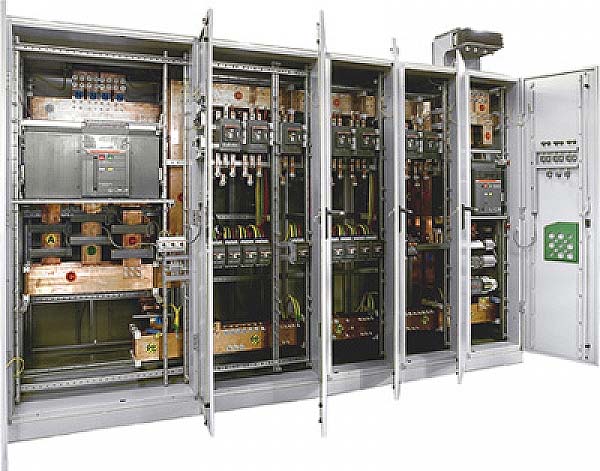
Главный распределительный щит (ГРЩ) на ток 6300 А
[http://www.uzoelectro.ru/catalogue/group-383/product-36465/ ]Тематики
- НКУ (шкафы, пульты,...)
- электроснабжение в целом
- электроустановки
Синонимы
EN
- feeder switchboard
- m.s.b.
- main distributing frame
- main distribution board
- main distribution switchboard
- Main Low Voltage Switchboard
- main low-voltage distribution switchboard
- main switchboard
- MLVS
- MSB
- power center
FR
комплектное устройство первичного распределения электроэнергии
-
[Интент]
Рис. ABBПараллельные тексты EN-RU
They are usually installed on the load side of MV/LV transformers or generators.
These assemblies include one or more incoming units, bus ties and a relatively reduced number of outgoing units.
There are also present measuring instruments and other switching and control equipment.
These assemblies have a sturdy structure to withstand the electrodynamic stresses and the weight of big sized apparatus.
As a matter of fact peculiar characteristics of the power center are high rated currents and shortcircuit currents.
The constructional type is a cubicle structure, with metal enclosure and sections divided into compartments with selective access.
[ABB]Такие устройства обычно подключают на стороне нагрузки СВ/НВ трансформаторов или генераторов.
В их состав входят один или несколько блоков ввода, шины и относительно небольшое число блоков вывода.
В состав комплектного устройства первичного распределения электроэнергии входят также измерительные приборы, коммутационные устройства и средства контроля состояния.
Данные комплектные устройства имеют прочную конструкцию, способную выдерживать электродинамическое действие токов и вес крупногабаритной аппаратуры.
Центры распределения электроэнергии характеризуются высокими номинальным током и током короткого замыкания.
С точки зрения конструктивного исполнения они представляют собой многошкафное комплектное устройство в металлической оболочке, состоящее из секций, каждая из которых разделена на отсеки с независимым доступом.
[Перевод Интент]Safety enclosed boards are used for most new installations. Common terms used to designate equipment of this type are metal-enclosed switchgear and metal-clad switchgear.
Most safety enclosed boards are of the unit or sectional type. They consist of a combination of the desired number and type of standardized unit sections.
Each section is a standard factory-assembled combination of a formed steel panel and apparatus mounted on a steel framework.
Safety enclosed switchgear may be classified with respect to purpose of application as follows:
1. General medium- or high-voltage switchgear
2. Primary unit substations
3. Rectifier unit substations
4. Secondary unit substations or power centers
5. General low-voltage switchgear
6. Low-voltage distribution switchboards
7. Motor-control-center switchboards
[American electricians’ handbook]Тематики
- НКУ (шкафы, пульты,...)
- комплектное распред. устройство (КРУ)
EN
Англо-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > power center
-
12 primary distribution switchgear
комплектное устройство первичного распределения электроэнергии
-
[Интент]
Рис. ABBПараллельные тексты EN-RU
They are usually installed on the load side of MV/LV transformers or generators.
These assemblies include one or more incoming units, bus ties and a relatively reduced number of outgoing units.
There are also present measuring instruments and other switching and control equipment.
These assemblies have a sturdy structure to withstand the electrodynamic stresses and the weight of big sized apparatus.
As a matter of fact peculiar characteristics of the power center are high rated currents and shortcircuit currents.
The constructional type is a cubicle structure, with metal enclosure and sections divided into compartments with selective access.
[ABB]Такие устройства обычно подключают на стороне нагрузки СВ/НВ трансформаторов или генераторов.
В их состав входят один или несколько блоков ввода, шины и относительно небольшое число блоков вывода.
В состав комплектного устройства первичного распределения электроэнергии входят также измерительные приборы, коммутационные устройства и средства контроля состояния.
Данные комплектные устройства имеют прочную конструкцию, способную выдерживать электродинамическое действие токов и вес крупногабаритной аппаратуры.
Центры распределения электроэнергии характеризуются высокими номинальным током и током короткого замыкания.
С точки зрения конструктивного исполнения они представляют собой многошкафное комплектное устройство в металлической оболочке, состоящее из секций, каждая из которых разделена на отсеки с независимым доступом.
[Перевод Интент]Safety enclosed boards are used for most new installations. Common terms used to designate equipment of this type are metal-enclosed switchgear and metal-clad switchgear.
Most safety enclosed boards are of the unit or sectional type. They consist of a combination of the desired number and type of standardized unit sections.
Each section is a standard factory-assembled combination of a formed steel panel and apparatus mounted on a steel framework.
Safety enclosed switchgear may be classified with respect to purpose of application as follows:
1. General medium- or high-voltage switchgear
2. Primary unit substations
3. Rectifier unit substations
4. Secondary unit substations or power centers
5. General low-voltage switchgear
6. Low-voltage distribution switchboards
7. Motor-control-center switchboards
[American electricians’ handbook]Тематики
- НКУ (шкафы, пульты,...)
- комплектное распред. устройство (КРУ)
EN
Англо-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > primary distribution switchgear
-
13 primary unit substation
комплектное устройство первичного распределения электроэнергии
-
[Интент]
Рис. ABBПараллельные тексты EN-RU
They are usually installed on the load side of MV/LV transformers or generators.
These assemblies include one or more incoming units, bus ties and a relatively reduced number of outgoing units.
There are also present measuring instruments and other switching and control equipment.
These assemblies have a sturdy structure to withstand the electrodynamic stresses and the weight of big sized apparatus.
As a matter of fact peculiar characteristics of the power center are high rated currents and shortcircuit currents.
The constructional type is a cubicle structure, with metal enclosure and sections divided into compartments with selective access.
[ABB]Такие устройства обычно подключают на стороне нагрузки СВ/НВ трансформаторов или генераторов.
В их состав входят один или несколько блоков ввода, шины и относительно небольшое число блоков вывода.
В состав комплектного устройства первичного распределения электроэнергии входят также измерительные приборы, коммутационные устройства и средства контроля состояния.
Данные комплектные устройства имеют прочную конструкцию, способную выдерживать электродинамическое действие токов и вес крупногабаритной аппаратуры.
Центры распределения электроэнергии характеризуются высокими номинальным током и током короткого замыкания.
С точки зрения конструктивного исполнения они представляют собой многошкафное комплектное устройство в металлической оболочке, состоящее из секций, каждая из которых разделена на отсеки с независимым доступом.
[Перевод Интент]Safety enclosed boards are used for most new installations. Common terms used to designate equipment of this type are metal-enclosed switchgear and metal-clad switchgear.
Most safety enclosed boards are of the unit or sectional type. They consist of a combination of the desired number and type of standardized unit sections.
Each section is a standard factory-assembled combination of a formed steel panel and apparatus mounted on a steel framework.
Safety enclosed switchgear may be classified with respect to purpose of application as follows:
1. General medium- or high-voltage switchgear
2. Primary unit substations
3. Rectifier unit substations
4. Secondary unit substations or power centers
5. General low-voltage switchgear
6. Low-voltage distribution switchboards
7. Motor-control-center switchboards
[American electricians’ handbook]Тематики
- НКУ (шкафы, пульты,...)
- комплектное распред. устройство (КРУ)
EN
Англо-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > primary unit substation
-
14 cloud
klaud
1. сущ.
1) облако;
мн.;
возв. небеса Clouds are commonly classified in four kinds, cirrus, cumulus, stratus, and nimbus. ≈ Облака обычно делятся на перистые, кучевые, слоистые и дождевые. Magellanic Clouds ≈ Магеллановы облака
2) облако, клубы (пыли, дыма и т. п.) to blow a cloud разг. ≈ курить mushroom cloud ≈ грибовидное облако (при атомном взрыве)
3) рой, тьма, туча( мошек, птиц и т. п.) ;
перен. множество, толпа cloud of witnesses ≈ множество свидетелей
4) все, что скрывает, затемняет: завеса, покров They break into our houses under cloud of night. ≈ Они ворвались в наши дома под покровом ночи. in the clouds
5) все, что омрачает, огорчает a cloud on one's reputation ≈ пятно на чьей-л. репутации to be under a cloud of suspicion ≈ быть под подозрением under a cloud ≈ в трудном положении, в беде;
с пятном на репутации
6) легкий свободно связанный шерстяной шарф
7) пятно ∙ to have one's head in the clouds, to be in the clouds ≈ витать в облаках in the clouds ≈ нереальный, воображаемый every cloud has a/its silver lining посл. ≈ нет худа без добра under a cloud
2. гл.
1) покрывать(ся) облаками, тучами
2) омрачать;
затемнять, затуманивать Syn: dim
2., obscure
2., darken
3) омрачаться
4) порочить, чернить, бросать тень( на репутацию) Syn: defame, asperse, sully
5) оттенять пятнами другого цвета The backs are gilt or rather clouded with gold. ≈ Спинки были позолоченные или, скорее, оттенены золотыми пятнами. ∙ cloud over cloud up облако, туча - the sun hidden by *s солнце, закрытое облаками - * bar гряда облаков, облачный вал - * break разрыв в облаках - * cover облачный покров - * deck облачный слой облако, клубы (дыма) - * of dust облако пыли - smoke * дымовое облако - * of electrons( физическое) электронное облако - * attack( военное) газобаллонная атака туча, масса, тьма - * of mosquitoes туча комаров - * of flies тьма мух покров;
завеса - under * of night под покровом ночи - a * of witnesses (библеизм) облако свидетелей;
множество очевидцев омрачающее, бросающее тень - * of war угроза войны - * on smb.'s happiness облачко, омрачающее счастье - * of grief облако грусти - * of suspicion тень подозрения - * on smb.'s reputation пятно на репутации (возвышенно) небо, небеса - to sail up into the *s взвиться в облака свободно связанный шерстяной женский шарф помутнение или жилка( в камне) (специальное) "облако" точек на диаграмме (специальное) пятно > * buster небоскреб;
скоростной самолет;
высокий мяч (баскетбол) > to blow a * курить табак, пускать облако дыма > to have one's head in the *s, to be in the *s витать в облаках > to drop from the *s как с неба свалился;
свалилось как снег на голову > to be lost in the *s запутаться( в аргументах) > to cast a * вызывать отчужденность > to be under a * быть под подозрением;
быть в немилости;
быть в тяжелом положении > every * has a silver lining и в плохом можно найти хорошее покрывать облаками, тучами - the moon is *ed луна закрыта облаками покрываться облакми, тучами, заволакиваться - the sky *ed over небо покрылось тучами омрачать - to * the spirits омрачить настроение затемнять - a mist *ed our view нам было плохо видно из-за тумана - his mind was *ed with suffering страдание затмило его рассудок омрачаться - her eyes *ed ее глаза затуманились - his face *ed with anger его лицо потемнело от гнева запятнать( репутацию) ;
очернить оттенять темными полосами или пятнами (химическое) мутнеть ~ шерстяная шаль;
to be (или to have one's head) in the clouds витать в облаках;
in the clouds нереальный, воображаемый ~ пятно;
a cloud on one's reputation пятно на (чьей-л.) репутации;
to be under a cloud of suspicion быть под подозрением cloud множество, тьма, туча (птиц, стрел и т. п.) ~ облако;
туча;
mushroom cloud грибовидное облако (при атомном взрыве) ;
clouds of smoke клубы дыма;
clouds of dust клубы пыли ~ омрачать(ся) ;
затемнять;
мутить ~ очернить;
запятнать (репутацию) ;
cloud over, cloud up заволакиваться ~ покров;
under cloud of night под покровом ночи ~ покрывать(ся) облаками, тучами ~ пятно;
a cloud on one's reputation пятно на (чьей-л.) репутации;
to be under a cloud of suspicion быть под подозрением ~ шерстяная шаль;
to be (или to have one's head) in the clouds витать в облаках;
in the clouds нереальный, воображаемый a ~ on one's happiness облачко, омрачающее (чье-л.) счастье ~ пятно;
a cloud on one's reputation пятно на (чьей-л.) репутации;
to be under a cloud of suspicion быть под подозрением ~ on title порок правового титула ~ очернить;
запятнать (репутацию) ;
cloud over, cloud up заволакиваться ~ очернить;
запятнать (репутацию) ;
cloud over, cloud up заволакиваться ~ облако;
туча;
mushroom cloud грибовидное облако (при атомном взрыве) ;
clouds of smoke клубы дыма;
clouds of dust клубы пыли ~ облако;
туча;
mushroom cloud грибовидное облако (при атомном взрыве) ;
clouds of smoke клубы дыма;
clouds of dust клубы пыли under a ~ под подозрением;
every cloud has a (или its) silver lining посл. = нет худа без добра ~ шерстяная шаль;
to be (или to have one's head) in the clouds витать в облаках;
in the clouds нереальный, воображаемый ~ облако;
туча;
mushroom cloud грибовидное облако (при атомном взрыве) ;
clouds of smoke клубы дыма;
clouds of dust клубы пыли under a ~ в немилости, в опале under a ~ в тяжелом положении under a ~ под подозрением;
every cloud has a (или its) silver lining посл. = нет худа без добра ~ покров;
under cloud of night под покровом ночи -
15 classification
- классификация (товаров)
- классификация (в информационных технологиях)
- классификация (в Service Manager 2010)
- классификация
- класс чистоты
классификация
Разделение множества объектов на подмножества по сходству или различию в соответствии с принятыми признаками.
[ГОСТ 1.1-2002]
классификация
1. Отнесение объектов, элементов некоторого множества к тому или иному классу (подмножеству, элементы которого характеризуются неким существенным признаком или группой существенных признаков); 2. Результат этого процесса. Существенный признак, по которому проводится К., называется ее основанием или критерием. Полученные в результате К. сведения об объекте называются номинальными данными. По своему смыслу К. представляет собой систему с иерархической структурой. Традиционно К. в естественных и технических науках подчиняется строгим правилам: а) в одной и той же К. применяется только одно основание, б) сумма подмножеств (классов) должна равняться классифицируемому множеству, в) ни один элемент одного подмножества (класса) не должен одновременно входить в другое подмножество (правило взаимоисключения), г) К. должна быть последовательной: включать все ступени иерархии, без «перес ка ки вания» через некоторые из них. Однако К. в общественных науках не всегда подчиняются приведенным правилам: они не имеют, например, исчерпывающего характера, предусмотренного правилом б), границы между классами в них размыты, неопределенны; критерии К. в них, как правило, являются многомерными: одни и те же характеристики могут быть свойственны разным классам и различия между ними прослеживаются лишь в совокупности характеристик, через их различные комбинации, приоритеты и соотношения. Здесь также более важен, чем в естественных науках, исторический аспект: постоянное взаимопересечение, изменение, возникновение и отмирание классов и самих классифицируемых явлений. В настоящее время быстро развиваются математико-ста тистические методы автоматической К. объектов с помощью ЭВМ. В их основе лежит анализ информации о каждом объекте, которая вводится в вычислительное устройство, и определение на ее основе, в соответствии с принятым «решающим правилом«, его принадлежности к тому или иному классу. См. Распознавание образов.
[ http://slovar-lopatnikov.ru/]Тематики
EN
классификация (в Service Manager 2010)
Размещение инцидента в иерархии дескрипторов, описывающих общую суть инцидента. Например, инцидент может быть классифицирован как относящийся к программному обеспечению, затем — к корпорации Майкрософт, а затем — к приложению Word 2003.
[ http://systemscenter.ru/scsm_help.ru/]EN
classification
The placement of an incident into a hierarchy of descriptors that indicate what the incident is generally about. For example, an incident could be classified as being related to software, and then to Microsoft, and then to Word 2003.
[ http://systemscenter.ru/scsm_help.ru/]Тематики
EN
классификация (в информационных технологиях)
Действие по назначению категории чему-либо. Классификация используется для обеспечения целостности в управлении и отчётности. КЕ, инциденты, проблемы, изменения и т.п., обычно классифицируются.
[Словарь терминов ITIL версия 1.0, 29 июля 2011 г.]EN
classification
The act of assigning a category to something. Classification is used to ensure consistent management and reporting. Configuration items, incidents, problems, changes etc. are usually classified.
[Словарь терминов ITIL версия 1.0, 29 июля 2011 г.]Тематики
EN
классификация (товаров)
Определение для изделия правильного кода в соответствии с таможенным тарифом в целях исчисления пошлины. В тех случаях, когда данная процедура становится очень сложной, нередко импортеры прибегают к судебным разбирательствам по вопросу правильности определения таможенной службой пошлин на данное изделие
[Упрощение процедур торговли: англо-русский глоссарий терминов (пересмотренное второе издание) НЬЮ-ЙОРК, ЖЕНЕВА, МОСКВА 2011 год]EN
classification
The placement of an item under the correct number in the customs tariff for duty purposes. At times this procedure becomes highly complicated; it is not uncommon for importers to resort to litigation over the correct duty to be assessed by the customs on a given item
[Trade Facilitation Terms: An English - Russian Glossary (revised second edition) NEW YORK, GENEVA, MOSCOW 2141]Тематики
EN
3.14 классификация (classification): Схема, в соответствии с которой информация подразделяется на категории с целью применения соответствующих защитных мер против этих категорий.
Примечание - Соответствующие защитные меры применяют для следующих категорий: возможность мошенничества, конфиденциальность или критичность информации.
Источник: ГОСТ Р ИСО/ТО 13569-2007: Финансовые услуги. Рекомендации по информационной безопасности
3.6 классификация (classification): Систематическая идентификация и упорядочение деловой деятельности и (или) документов по категориям в соответствии с логически структурированными условиями, методами и процедурными правилами, представленными в классификационной системе.
Источник: ГОСТ Р ИСО 15489-1-2007: Система стандартов по информации, библиотечному и издательскому делу. Управление документами. Общие требования оригинал документа
3.14 классификация (classification): Схема, в соответствии с которой информация подразделяется на категории с целью применения соответствующих защитных мер против этих категорий.
Примечание - Соответствующие защитные меры применяют для следующих категорий: возможность мошенничества, конфиденциальность или критичность информации.
Источник: ГОСТ Р ИСО ТО 13569-2007: Финансовые услуги. Рекомендации по информационной безопасности
3.2 классификация (classification): Обозначение газа или газовой смеси, включающее номер настоящего стандарта и группу индексов (основную группу и подгруппу), идентифицирующих газ или газовую смесь.
Примечание - Группы индексов приведены в 5.1 (см. таблицу 2).
Источник: ГОСТ Р ИСО 14175-2010: Материалы сварочные. Газы и газовые смеси для сварки плавлением и родственных процессов оригинал документа
2.30 класс чистоты (classification): Уровень чистоты (2.32) воздуха по взвешенным в воздухе частицам, применимый к чистому помещению (2.33) или чистой зоне (2.34), выраженный в терминах «Класс N ИСО», который определяет допустимые концентрации (частиц (2.102) в кубическом метре (частиц/м3)) для заданных диапазонов размеров частиц.
Примечания
1 Концентрацию определяют по уравнению (1) ИСО 14644-1:1999, статья 3.2.
2 В соответствии с ИСО 14644-1:1999 классы чистоты ограничены диапазоном от класса 1 ИСО до класса 9 ИСО.
3 Пороговые значения размеров частиц (2.105) (нижние пороговые значения), применяемые для классификации по настоящему стандарту, находятся в диапазоне 0,1-5,5 мкм. Для пороговых размеров частиц, находящихся вне этого диапазона, чистота (2.32) воздуха может быть определена (но не классифицирована) с помощью U-дескрипторов (2.136) или М-дескрипторов (2.89).
4 Промежуточные классификационные числа могут быть определены с наименьшим допустимым приращением 0,1, т. е. диапазон промежуточных классов ИСО увеличивается от класса 1,1 ИСО до класса 8,9 ИСО.
5 Класс чистоты может быть определен для любого из трех состояний чистых помещений (см. 2.17, 2.18, 2.97).
[ИСО 14644-1:1999, статья 2.1.4]
Источник: ГОСТ Р ИСО 14644-6-2010: Чистые помещения и связанные с ними контролируемые среды. Часть 6. Термины оригинал документа
3.5.3 классификация (classification): Процесс распределения абстракций в структуре, организованной в соответствии с их отличительными свойствами.
Источник: ГОСТ Р ИСО 15531-31-2010: Системы промышленной автоматизации и интеграция. Данные по управлению промышленным производством Часть 31. Информационная модель ресурсов оригинал документа
3.42 классификация (classification): Процесс выстраивания абстракций в структуру, организованную в соответствии с их отличительными свойствами, взаимосвязями и поведением.
Источник: ГОСТ Р 54136-2010: Системы промышленной автоматизации и интеграция. Руководство по применению стандартов, структура и словарь оригинал документа
Англо-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > classification
-
16 cloud
[klaud] 1. сущ.1) облако; тучаThe sky became dark with clouds and it began to rain heavily. — Набежали чёрные тучи, и пошёл проливной дождь.
Clouds are commonly classified in four kinds, cirrus, cumulus, stratus, and nimbus. — Облака обычно делятся на перистые, кучевые, слоистые и дождевые.
2) облако, клубы (пыли, дыма)to blow a cloud — разг. курить
3) рой, тьма, туча; множество, толпа4) завеса, покровThey break into our houses under cloud of night. (W. Scott, The Fair Maid of Perth, 1831) — Они ворвались в наши дома под покровом ночи.
5) ( clouds) поэт. небеса, небо6) нечто омрачающее; изъян, пятно, червоточинаa cloud on one's reputation — пятно на чьей-л. репутации
7) лёгкий, свободно связанный шерстяной шарф8) тех. пятно••to have one's head in the clouds, to be in the clouds — витать в облаках
- in the clouds 2. гл.Every cloud has a / its silver lining. — посл. Нет худа без добра.
1)а) покрывать облаками, тучамиб) = cloud over покрываться облаками, тучами, заволакиватьсяThe sky has clouded over, we shan't see the sun again today. — Небо затянуло тучами, сегодня больше не будет солнца.
2)а) омрачать; затемнять, затуманиватьSyn:б) = cloud over омрачатьсяMary's face clouded over when she heard the bad news about her mother's operation. — Лицо Мэри померкло от огорчения, когда она узнала, что её мать прооперировали неудачно.
в) = cloud over / up мутнеть, затуманиватьсяThe windows have clouded over in the steam. — Окна запотели.
3) порочить, чернить, бросать тень ( на репутацию)Syn:The backs were gilt or rather clouded with gold. — Спинки были позолоченные или, скорее, оттенённые золотом.
См. также в других словарях:
Classified advertising — Classified ads in a newspaper. Classified advertising is a form of advertising which is particularly common in newspapers, online and other periodicals which may be sold or distributed free of charge. Advertisements in a newspaper are typically… … Wikipedia
classified directory — ˌclassified diˈrectory noun [countable] COMMERCE a list of all the names, addresses, and telephone numbers of companies in a particular area, which is usually organized according to the type of business : • a classified directory of companies… … Financial and business terms
Classified information in the United States — For information on practices in other countries, see Classified information. The United States government classification system is currently established under Executive Order 13526, the latest in a long series of executive orders on the topic.[1] … Wikipedia
Classified information — Top Secret redirects here. For other uses, see Top Secret (disambiguation). Unclassified redirects here. See also, Unclassified (album). State secrets redirects here. See also, state secrets privilege. A typical classified document. Page 13 of a… … Wikipedia
Classified Board — Also known as Staggered Board: is one in which the directors are placed into different classes and serve overlapping terms. Since only part of the board can be replaced each year, an outsider who gains control of a corporation may have to wait a… … Financial and business terms
Classified information in the United Kingdom — Classified information in the United Kingdom, now called Protectively Marked Information, is a system used to protect information from intentional or inadvertent release to unauthorised readers. The system is organised by the Cabinet Office and… … Wikipedia
Classified pricing — is the pricing system of federal milk marketing orders, under which milk processors pay into a pool for fluid grade (Grade A) milk. The price that processors have to pay into the pool is based on how the milk ultimately is used. Milk used for… … Wikipedia
classified ad — noun a short ad in a newspaper or magazine (usually in small print) and appearing along with other ads of the same type • Syn: ↑classified advertisement, ↑classified • Hypernyms: ↑newspaper ad, ↑newspaper advertisement • Hyponyms: ↑ … Useful english dictionary
Classified Shares — The separation of company equity into more than one class of common shares, usually called Class A and Class B. Also known as classified stock . The specific features of each class are set out in the corporate charter and bylaws. Voting… … Investment dictionary
classified stock — The division of stock into more than one class of common stock, usually called Class A and Class B. The specific features of each class, which are set out in the charter and bylaws, usually give certain advantages to the Class A shares, such as… … Financial and business terms
Functionally classified barn — A functionally classified barn is a barn whose style is best classified by its function. Barns which do not fall into one of the broader categories of barn styles, such as English barns or crib barns, can best be classified by some combination of … Wikipedia
